Isolator Technology: A Breakthrough in Aseptic Processing for Safer Medicines
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, ensuring medicines are produced in a sterile, contamination-free environment is critical—particularly for injectables, also known as parenteral drugs. Even the slightest impurity can put patients at risk and lead to costly recalls. Traditionally, cleanrooms and airflow systems have been the backbone of aseptic processing. However, recent advancements in isolator technology are raising sterility standards by creating a fully enclosed, contamination-free workspace that offers a reliable barrier against contaminants, easier to control than traditional cleanrooms.
Curious about how isolators are transforming aseptic processing and contributing to safer medicines? Let’s explore this cutting-edge technology in detail.
Understanding Isolator Technology in Aseptic Processing
Isolator technology is a specialized barrier system that creates a completely sealed environment around a product or process, protecting it from contamination by external particles, bacteria, or human contact. Unlike cleanrooms, which control the environment of an entire room, isolators focus solely on the immediate space around the product, providing a higher level of sterility where it matters most.
This technology uses advanced decontamination methods, such as Vaporized Hydrogen Peroxide (VHP), to sterilize the isolator’s internal environment, maintaining ultra-clean conditions. By minimizing human interaction and creating a physical barrier around sensitive processes, isolators significantly reduce contamination risks and increase consistency in aseptic processing.
Types of Barrier Systems: RABS and Isolators
Barrier systems are essential in pharmaceutical manufacturing to maintain aseptic conditions. There are two primary types of barrier systems: Restricted Access Barrier Systems (RABS) and isolators. Each offers unique configurations suited for different manufacturing environments and sterility needs.
1. Restricted Access Barrier Systems (RABS)
Restricted Access Barrier Systems (RABS) provide a semi-enclosed workspace for aseptic processing, balancing contamination control with accessibility. RABS are ideal for processes where full containment is not essential but where a controlled, sterile environment is still critical.
- oRABS (Open RABS): Open RABS allow controlled airflow from the surrounding cleanroom, helping maintain cleanliness around the product. This configuration is suitable for lower-risk aseptic processing tasks. Within oRABS, there are two subtypes:
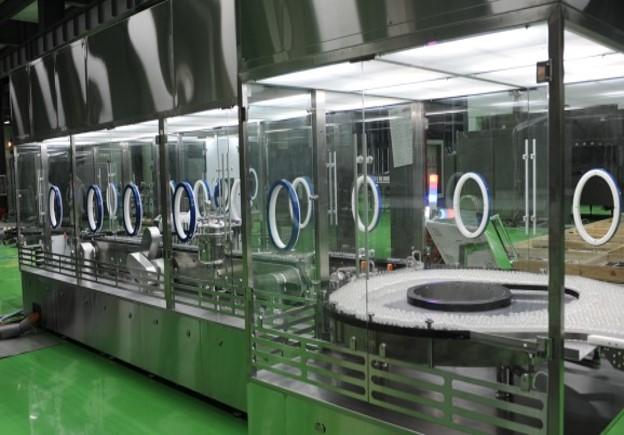

- Active oRABS: These systems include their own airflow system to maintain positive pressure, offering enhanced sterility assurance.
- Passive oRABS: Relying on cleanroom airflow, Passive oRABS are simpler and more cost-effective, ideal for basic aseptic tasks.
- cRABS (Closed RABS): Closed RABS fully enclose the workspace and often operate under negative pressure, providing a higher level of contamination control than open RABS. Closed RABS are suitable for more sensitive processes where sterility is paramount but full isolation is not required.
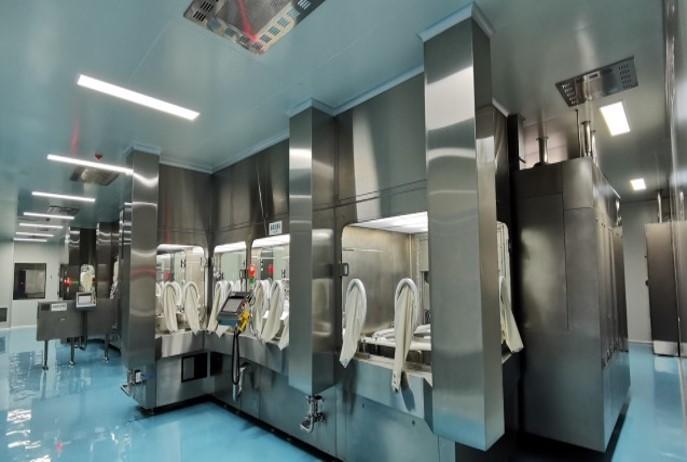

2. Isolators
Unlike RABS, isolators create a completely sealed environment, achieving the highest level of sterility and reducing dependency on the surrounding cleanroom environment. Isolators are especially suitable for high-risk or sensitive products, as they completely isolate the product from external contaminants.
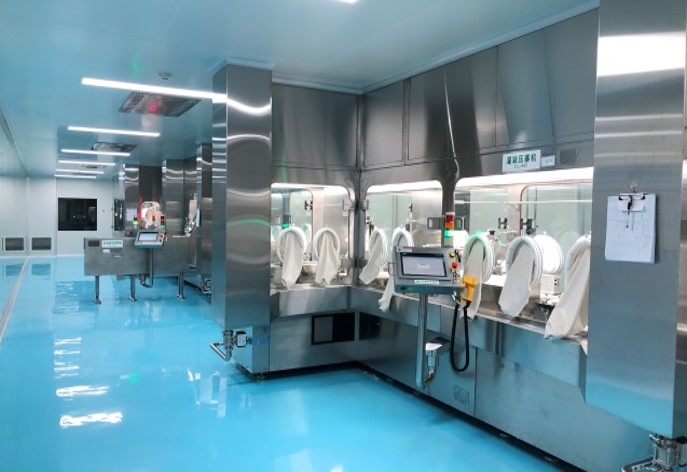

- Open Isolator: Open isolators allow limited controlled air exchange with the cleanroom, protecting the product while enabling some interaction with the external environment. They are used in processes where contamination risks are lower, but sterility is still crucial.
- Closed Isolator: Closed isolators are fully sealed and often operate under negative pressure with specialized filters. This configuration is critical for handling highly potent or hazardous compounds, as it provides the highest containment level, protecting both operators and the environment. Closed isolators are ideal for high-risk aseptic processes requiring maximum containment and sterility.
The Evolution of Aseptic Processing: From Cleanrooms to Isolator Technology
Over the years, aseptic processing has undergone significant transformations. Initially, cleanrooms and airflow systems provided basic contamination control but couldn’t entirely eliminate risks associated with human error. In the 1980s and 1990s, isolator technology was introduced, primarily for sterility testing. As isolators evolved, they became indispensable in complex manufacturing processes like vial filling and syringe assembly, where a contamination-free environment is critical.
Today, isolator technology for pharmaceutical applications has become a cornerstone of modern aseptic processing, offering reliable sterility assurance across various stages of production.
Key Benefits of Isolator Technology for Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Implementing isolator technology in aseptic processing brings numerous benefits to pharmaceutical manufacturers, enhancing sterility and safety:
- Enhanced Sterility Assurance: Isolators create a fully enclosed environment, significantly reducing contamination risks, especially important for injectable drugs and other high-risk pharmaceuticals.
- Reduced Dependency on High-Grade Cleanrooms: Since isolators maintain sterility within their own enclosure, they minimize the need for stringent cleanliness in surrounding areas. This can lead to cost savings by reducing HVAC demands and cleanroom maintenance.
- Increased Operator Safety: When handling potent or hazardous compounds, isolators shield operators from exposure, improving workplace safety.
- Minimal Human Interaction: Isolator systems use glove ports or automated systems, reducing direct human contact with the product. This not only lowers contamination risk but also minimizes human error.
- Cost Efficiency Over Time: Although isolators may have a higher upfront cost, they provide long-term savings by minimizing contamination risks, reducing cleanroom maintenance costs, and streamlining production processes.
Regulatory Compliance with Isolator Technology
As global regulatory standards grow more stringent, the demand for isolator technology in pharmaceutical manufacturing is increasing. In Europe, the updated EU GMP Annex 1 guidelines emphasize advanced contamination control and advocate for technologies that reduce human intervention in sterile environments.
Isolator systems align perfectly with these requirements, creating fully enclosed, controlled environments with robust sterility assurance. This technology supports compliance with EU GMP Annex 1, particularly for processes involving high-potency drugs that require high levels of sterility and containment. By using isolators, pharmaceutical manufacturers can meet the standards set by regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA, ensuring product safety and quality.
As isolator technology advances, it is set to play an increasingly critical role in pharmaceutical manufacturing. With its ability to provide reliable contamination control, meet stringent regulatory requirements, and support a safer working environment, isolator technology paves the way for producing safer, higher-quality medicines. This technology helps pharmaceutical manufacturers meet global standards and ensures that patients receive the safest products possible.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PharmTech EU's Partnership with Tofflon: Delivering Advanced Isolator Solutions
At PharmTech EU, we are dedicated to helping the pharmaceutical industry achieve cleaner, safer manufacturing environments. Through our partnership with Tofflon, a leader in pharmaceutical equipment, we provide advanced isolator solutions tailored to diverse facility needs.
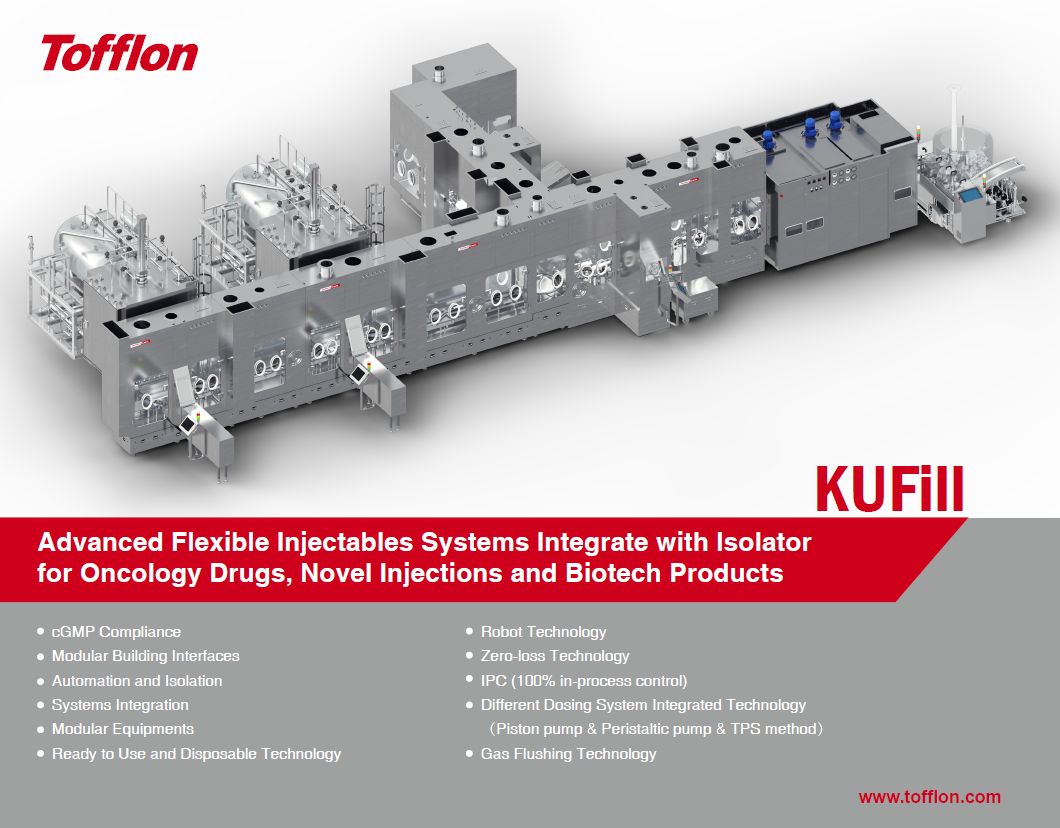
One standout product is Tofflon's KUFill system, an isolator-integrated solution for aseptic injection that combines flexibility, modularity, and speed to support efficient, safe production. KUFill aligns with regulatory requirements and offers a streamlined solution for aseptic processing, meeting high sterility and containment standards.
Whether you're expanding an existing facility or establishing new aseptic processes, PharmTech EU and Tofflon provide the expertise, equipment, and support needed to achieve the highest sterility standards in manufacturing. By incorporating isolator technology, your facility can meet regulatory demands, enhance operator safety, and ensure product quality for a contamination-free production environment.